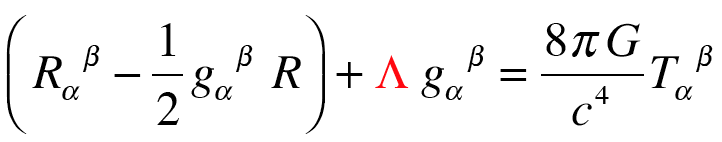“`html
Exploring the Cosmos: The Role of Space Telescopes in Astrophysics
As a fervent advocate for science and technology with a deeply rooted interest in physics and astronomy, I’ve always been captivated by the mechanisms we use to unravel the mysteries of the cosmos. Among these, space telescopes stand out as monumental achievements in our quest for knowledge. Their ability to bypass the Earth’s atmosphere provides us with clear, unparalleled views of the universe.
The Science Behind Space Telescopes
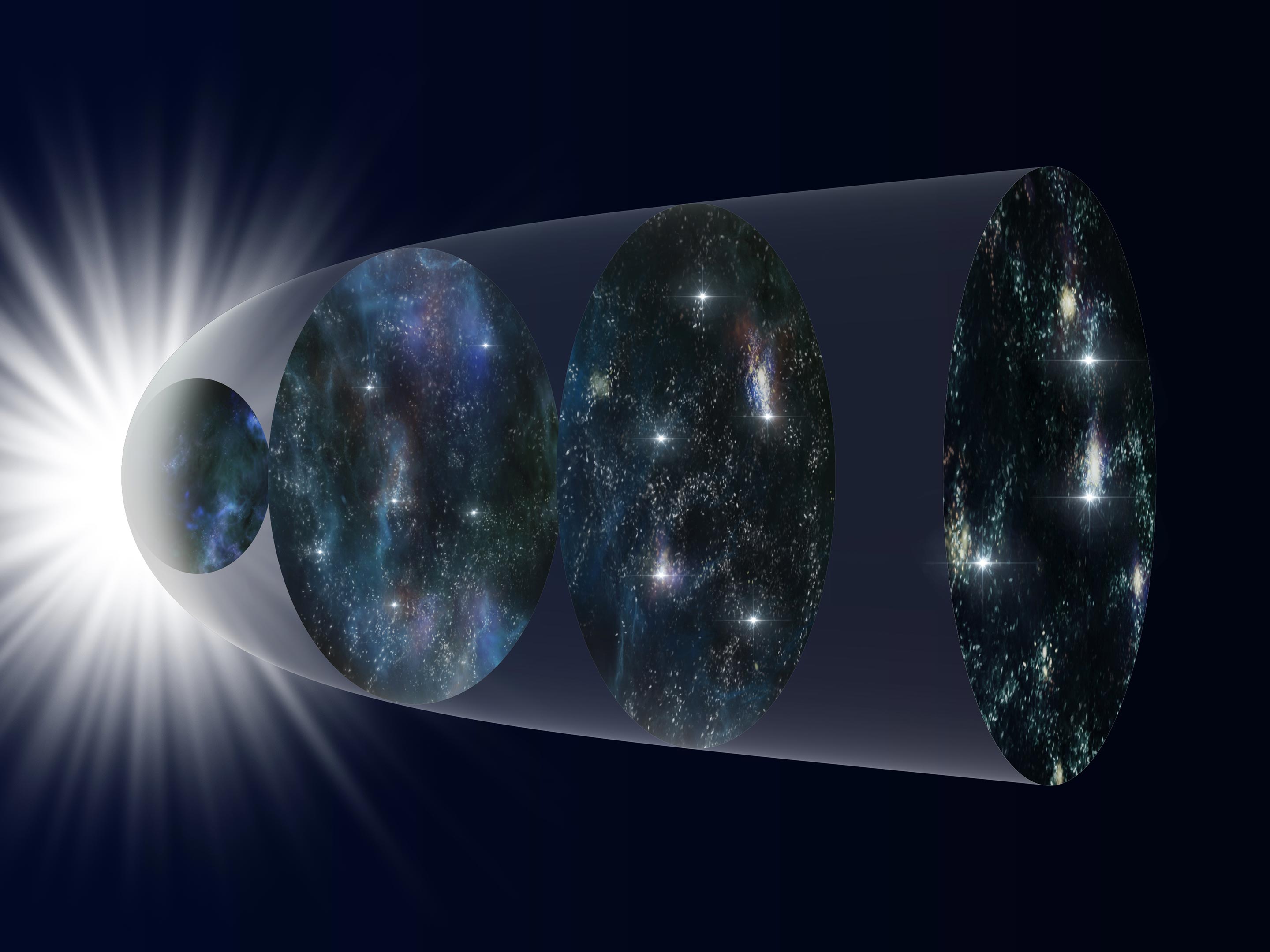
Space telescopes, orbiting outside the Earth’s atmosphere, open a window to the universe that ground-based telescopes cannot match. The fundamental science behind these observatories is their capacity to collect electromagnetic radiation (light, X-rays, infrared, etc.) from celestial objects without the interference of the Earth’s atmospherics. This advantage allows for sharper images and the study of cosmic phenomena at wavelengths that are otherwise absorbed or scattered before reaching the Earth’s surface.
< >
>
Why Space Telescopes?
The primary advantage of space telescopes lies in their ability to observe the universe across different electromagnetic spectra, many of which do not reach the Earth’s surface due to atmospheric absorption. For instance, telescopes like Hubble have been instrumental in capturing detailed images of distant galaxies, contributing to our understanding of their structure and formation. Moreover, instruments like the James Webb Space Telescope allow astronomers to peer back in time, observing the light from the first galaxies that formed after the Big Bang.
Technological Marvels: The Hubble and James Webb Space Telescopes
Launched in 1990, the Hubble Space Telescope has provided some of the most detailed images of distant galaxies, nebulae, and other astronomical phenomena. By orbiting outside Earth’s atmosphere, Hubble has avoided the blurring effects of air, furnishing images of unprecedented clarity and detail.
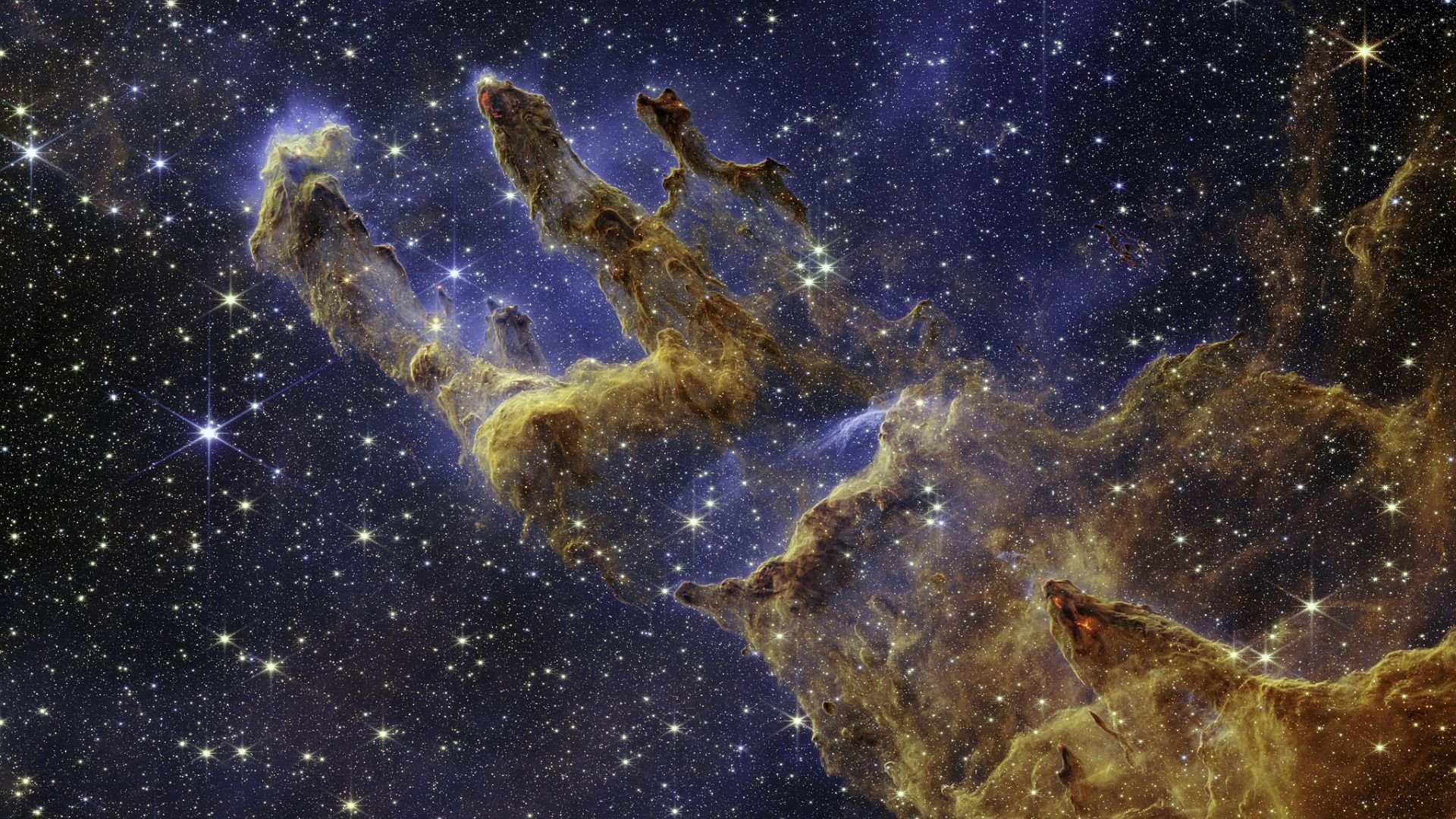
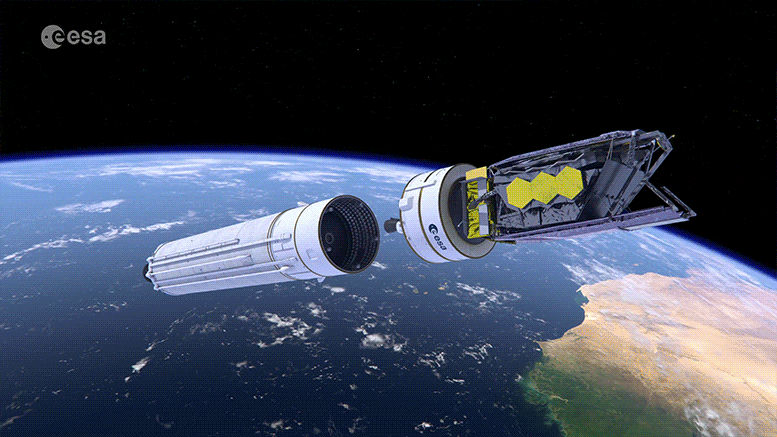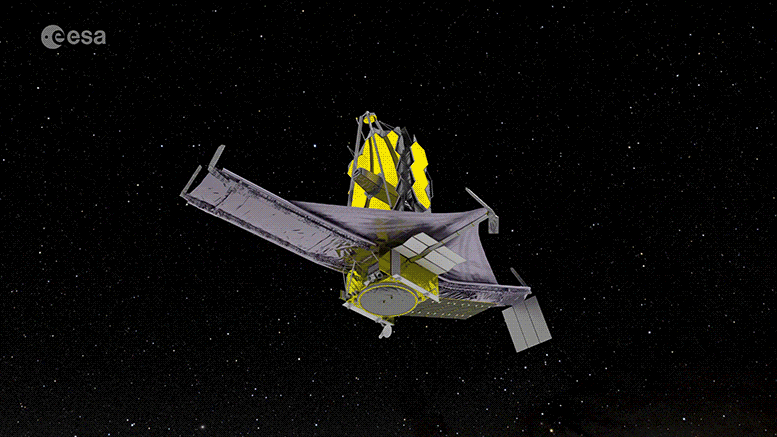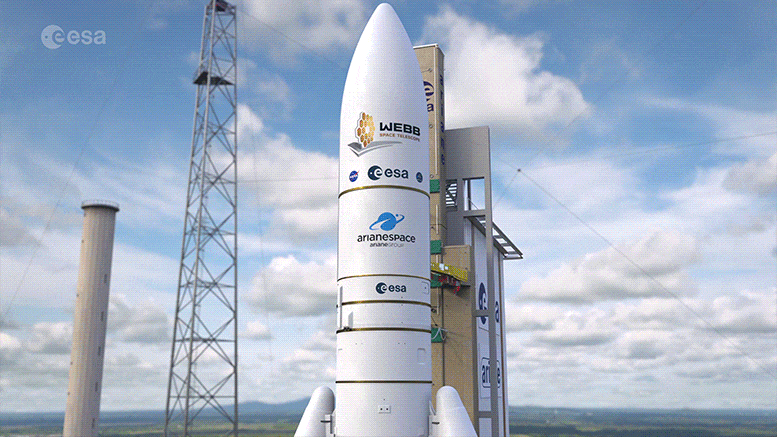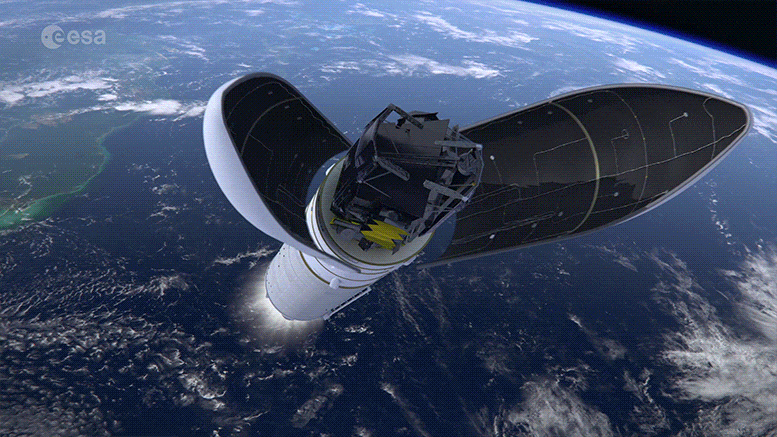
In contrast, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), launched in late 2021, represents the next-generation of space observatories. Equipped with a larger mirror than Hubble’s and sensitive instruments for infrared astronomy, JWST can observe the universe in ways Hubble cannot, such as peering through dust clouds to see stars forming inside.
< >
>
The Benefits of Observing in Infrared
One of the critical capacities of JWST is its ability to observe in infrared. This spectrum is key for looking back at the early universe, as the light from the first stars and galaxies has been redshifted (stretched) into infrared wavelengths due to the universe’s expansion. By observing in this spectrum, JWST can study the formation of the first galaxies, star systems, and even the conditions of potentially habitable exoplanets.
Impact on Modern Astrophysics
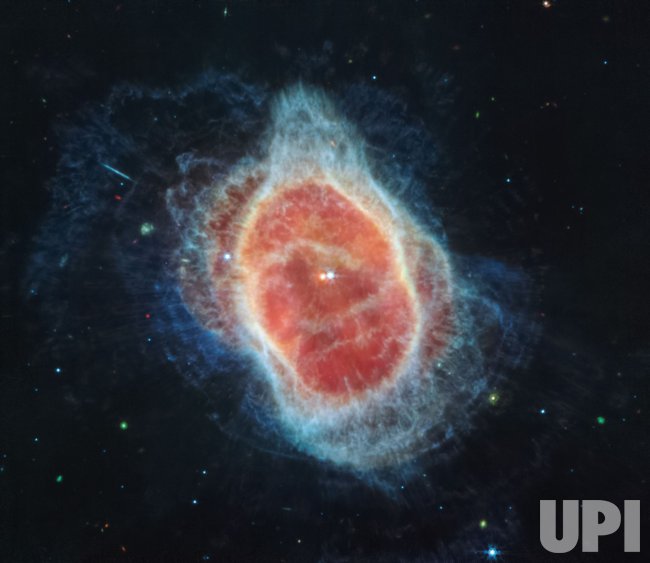
The contributions of space telescopes to science are immeasurable. They have not only expanded our understanding of the universe but have also pushed the boundaries of technology, leading to advancements in optics, materials science, and robotics. Observations from Hubble and JWST continue to challenge our theories of cosmology, pushing us toward new discoveries about dark energy, dark matter, and the ultimate fate of the universe.
< >
>
Final Thoughts
As someone deeply passionate about the intersection of technology and exploration, the advancements and discoveries made possible by space telescopes hold a special place in my heart. They embody the pinnacle of human curiosity and the relentless pursuit of knowledge. Each image captured and transmitted back to Earth not only adds a piece to the puzzle of our universe’s grand narrative but also serves as a reminder of what we can achieve when we reach for the stars.
“`