Leading Innovation: The Autodesk Revolution in Sustainable Design
In a recent episode of Fortune’s Leadership Next podcast, Andrew Anagnost, President and CEO of Autodesk, shared fascinating insights on the intersection of AI, sustainability, and the future of building and design. Autodesk, renowned for its innovative software solutions for those who create and design almost everything around us, is spearheading a transformation in how we approach sustainability and efficiency in building and manufacturing. Anagnost’s journey to the helm of Autodesk, marked by what he describes as joining the company as part of a “rebel group,” underscores the transformative power of innovative leadership in tech.
The Role of AI in Shaping a Sustainable Future
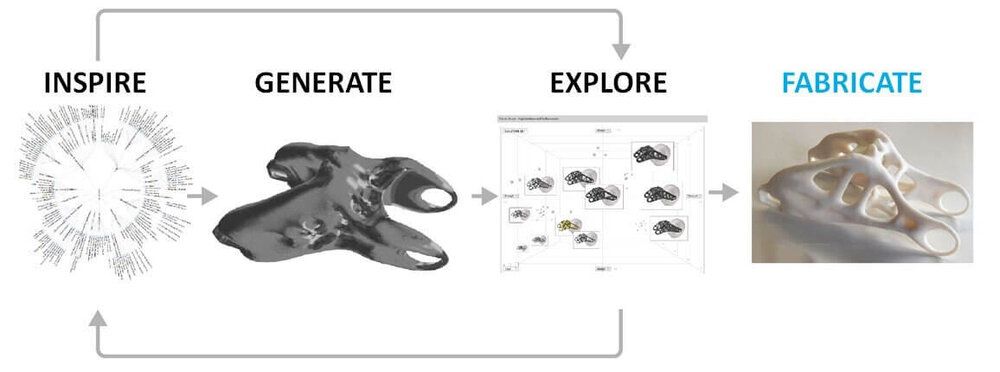
Autodesk’s use of AI is not just about enhancing design capabilities; it’s fundamentally about solving real-world problems. Anagnost elaborates on Autodesk’s use of generative design, a form of AI that can generate design options based on specific constraints. This innovation stands at the forefront of tackling some of the most pressing issues of our time, including climate change and the urgent need for sustainable housing solutions.
By enabling architects and designers to optimise for energy efficiency, reduce material waste, and even explore novel materials like industrial fungus for building siding, Autodesk is paving the way for more sustainable and affordable building projects. “Imagine building with materials that store carbon, or creating detailed representations that eliminate construction waste,” Anagnost muses, highlighting the potential for revolutionary change in the construction industry.
< >
>
< >
>
Navigating the Ethical Implications of AI
However, Anagnost doesn’t shy away from addressing the ethical considerations that come with the broad application of AI technology. Reflecting on the lessons learned from the social media era, he cautions against a future where AI becomes disconnected from human-centric needs. Drawing parallels to past regulatory interventions that safeguarded public interests, such as the telecommunications industry, he advocates for policies that ensure AI serves humanity’s best interests. “Owning your digital record should be a fundamental right,” he asserts, emphasizing the importance of aligning AI development with ethical standards.
<
>
Andrew Anagnost: A Visionary Leader
Anagnost’s own backstory, from a self-described “problematic teenager” to a leading figure in tech, underscores the importance of resilience, adaptability, and mentorship in achieving success. His journey reflects a belief in the potential for personal growth and the power of constructive feedback. As the head of Autodesk, he embodies the principles of forward-thinking and continuous innovation, driven by a passion for empowering creators and designers to shape a better world.
His leadership style, influenced by both of his predecessors and rooted in a love for engineering and design, has played a crucial role in Autodesk’s ability to reinvent itself consistently. By fostering a culture of innovation and advocating for the responsible use of AI, Anagnost is not only steering Autodesk towards a brighter future but also setting a precedent for how tech companies can contribute to solving global challenges.
Conclusion
Andrew Anagnost’s discussion on the Leadership Next podcast illuminates the pivotal role of AI in addressing sustainability and the ethical dimensions of technological advancement. Through its commitment to innovation, Autodesk exemplifies how technology can be harnessed to create positive change, guided by visionary leadership. As tech continues to evolve, it’s clear that the values and decisions of those at the helm will significantly shape our collective future.
For those interested in the transformative power of machine learning and AI’s potential to revolutionize industries for the better, Autodesk’s journey under Anagnost’s leadership offers valuable insights and inspiration.
 >
> >
>