As someone who has spent years in tech innovation, I am constantly amazed by the power of computational simulations to illuminate complex and dangerous scenarios. Recently, a groundbreaking study on wildfire simulation has redefined how we can analyze and potentially mitigate the devastating consequences of uncontrolled fires. This innovation isn’t just about numbers—it’s about saving lives, protecting ecosystems, and learning how to coexist responsibly with nature.
Why Wildfires Are So Unpredictable
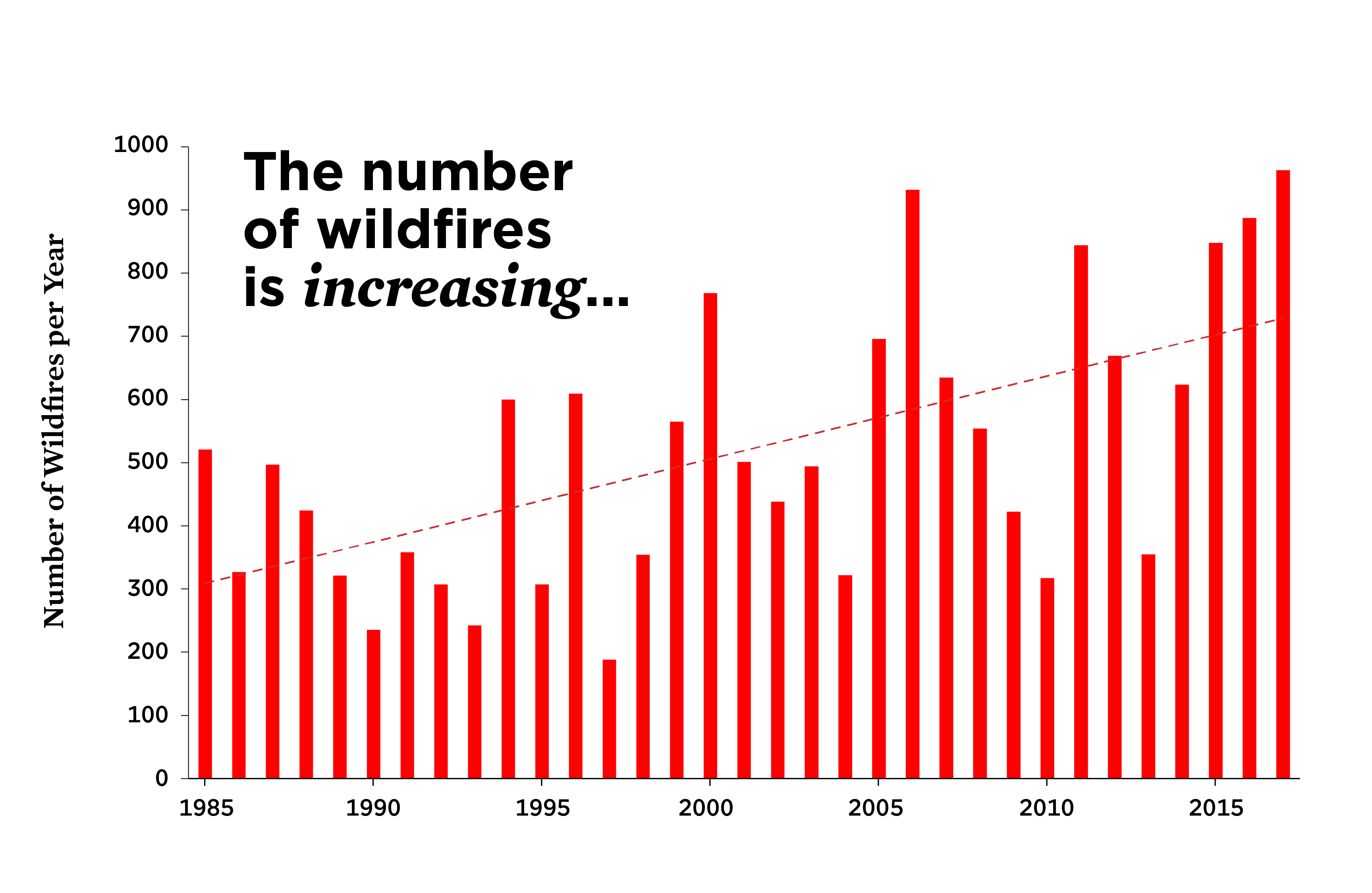
Wildfires are notorious for their chaos and destructive nature. By their very essence, wildfires feed on everything in their path: grasses, wood, shrubs, decomposing organic material—you name it. When conditions align, these fuels transform an ignited brushfire into an unstoppable inferno within moments. One of the most catastrophic cases occurred during the 2019 Australian bushfire season, which led to the loss of over one billion animals and a devastating impact on local ecosystems.
The key challenge in wildfire management lies in their unpredictability. Embers can travel miles, igniting new hotspots far from the initial blaze, and environmental factors like fuel distribution, moisture, and wind speed exacerbate the situation. These variables are notoriously difficult to model—until now.
The Power of High-Fidelity Wildfire Simulations
This new research offers an incredibly detailed simulation framework for wildfires, capable of modeling various types of terrains, vegetation, and environmental conditions. For instance, a fire on a savannah behaves vastly differently compared to one in a tropical rainforest. Unlike savannah fires, which spread rapidly across dry grasses and shrubs, rainforest fires face natural mitigation from higher moisture and tree vapor, limiting their scope.
Thanks to this simulation, we can now explore scenarios like:
- How varying moisture content in grasses affects fire intensity.
- The differences in fire behavior based on forest biomass height.
- How vegetation management in forests can prevent catastrophic crown fires.
One of the most awe-inspiring aspects of this research is its ability to distinguish between contained fires on the forest floor and large-scale crown fires, where entire trees ignite. By integrating data on vegetation types, moisture levels, and wind dynamics, this simulation provides actionable insights for improving fire management strategies.
A Game-Changer in Predicting the Unpredictable
What makes this simulation truly revolutionary is its predictive power. Unlike traditional methods, where humans relied on past case studies and estimate-driven decisions, this model enables us to simulate real-world wildfire scenarios safely. For instance, researchers tested their tool against actual burn experiments, and the results were strikingly close, bringing us one step closer to anticipating and controlling wildfires in the future.
A critical component of the simulation is analyzing embers—hot particles carried by high-speed winds that ignite new fires wherever they land. The simulation accounts for this chaotic variable, giving fire management teams a clearer understanding of where and how to deploy resources effectively.
Additionally, this tool doesn’t just highlight the risks but offers hope. It demonstrates how proactive vegetation management, like clearing dry, uneven biomass or introducing fire-resistant plants, could significantly reduce fire spreads. The balance of risk assessment and solution-oriented capabilities makes this simulation a significant step forward.
Applications and Implications
The potential applications of this wildfire simulation tool are vast:
| Application | Impact |
|---|---|
| Forest Management | Designing vegetation layouts to minimize crown fires. |
| Urban Planning | Building firebreaks and safe zones in vulnerable areas. |
| Insurance Modeling | Assessing wildfire risks for property underwriting. |
| Climate Change Research | Understanding how shifting conditions impact fire behavior. |
For climate researchers, this simulation could shed light on the role of warming temperatures in exacerbating fire risks. For urban planners, it offers tools to design fire-resistant communities. And in education, it serves as a powerful visual aid to help students and policymakers grasp the intricacies of fire behavior.
The Future of Wildfire Simulation
While the researchers’ work represents an incredible milestone, it’s important to note its limitations. Current iterations rely on pre-existing environmental and vegetation data, meaning accuracy can waver in poorly studied regions. However, future integration with AI (a field I’ve worked extensively in) might allow the model to adapt dynamically by analyzing real-time satellite data, weather reports, and historical trends.
Moreover, open access to the research means innovation won’t stop here. As the authors generously made their work freely available, other researchers and companies can expand on this foundation to unlock untold possibilities. For me, this is the pinnacle of technology’s potential: using data, simulations, and collaboration for the well-being of humanity and our planet.
Conclusion
As someone fascinated by how technology shapes our understanding of the natural world, I find this wildfire simulation tool to be an extraordinary achievement. It combines computational brilliance with a strong environmental mission, showing us how we can tackle the complex problems of our era. From savannahs to rainforests, the ability to predict wildfire behavior could redefine how societies worldwide prepare for and respond to these disasters. What a remarkable time to witness science, technology, and human ingenuity come together for a better tomorrow.
For those interested in innovation and our planet’s survival, this research should make its way to the top of your reading list. If you’d like to discuss how simulations like these could integrate with other AI-driven solutions or cloud platforms, feel free to reach out—I’ve seen firsthand how transformative technology can be when applied with purpose.
Focus Keyphrase: Wildfire Simulation

“`