Databases: NoSQL vs SQL
The two main types of modern databases to choose from are relational and non-relational, also known as SQL or NoSQL (for their query languages). There are a few main differences to be familiar with when deciding which database works best for your needs.
Relational Databases (also known as RDBMS and SQ Databases)
Relational databases (RDBMS) have been around for a good 45 years. In the past, they’ve worked well, for the times when data structures were much simpler and more static. In a relational database, you are required to define your schema before adding data to the database. Relational databases are table-based, and were built during a time that data was mostly structured and clearly defined by their relationship
Examples include MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, MongoDB, Redis
NoSQL
As informational and big data applications advanced, the traditional relational or SQL-based database was couldn’t really handle rapidly expanding data volumes and the growing complexities of data structures. Over the past 15 years, the non-relational, NoSQL databases became more popular for offering a more flexible, scalable, cost-efficient, alternative to the traditional SQL-based relational databases.
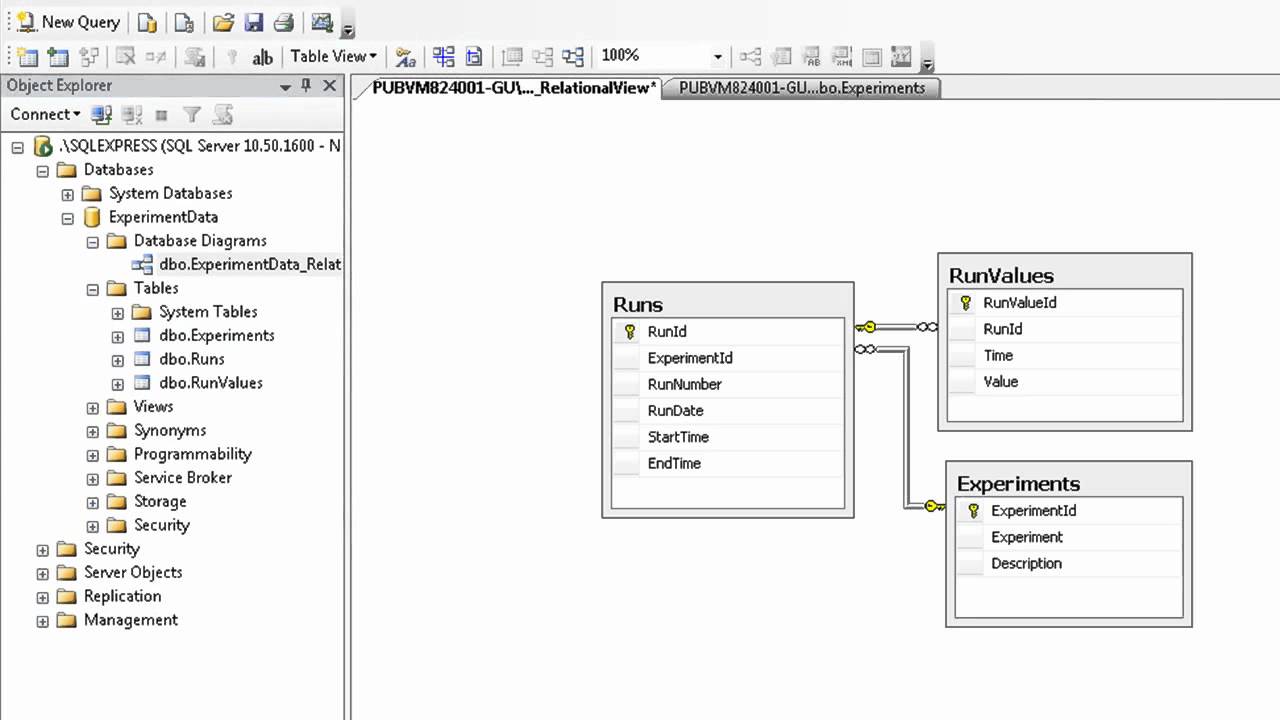
NoSQL databases feature dynamic schema, and allow you to use what’s known as “unstructured data.” This means you can build your application without having to first define the schema. Not needing a predefined schema makes NoSQL databases much easier to update as data and requirements change. Changing the schema structure in a relational database can be extremely expensive, time-consuming, and often involve downtime or service interruptions. NoSQL databases can be document based, graph databases, key-value pairs, or wide-column stores. NoSQL databases are designed to handle the more complex, unstructured data, (such as texts, social media posts, photos, videos, email) which increasingly make up much of the data that exists today.
Relational databases are vertically scalable but typically expensive. Since they require a single server to host the entire database, in order to scale, you need to buy a bigger, more expensive server. Scaling a NoSQL database is much cheaper, compared to a relational database, because you can add capacity by scaling horizontally over cheap, commodity servers.
Google Cloud datastore is a highly scalable low latency NoSQL database. It is built on top of Bigtable and Google Megastore. It provides the scalability of a NoSQL database and features of a relational database providing both strong consistency guarantee and high availability.
- Document databases store data in documents similar to JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) objects. Each document contains pairs of fields and values. The values can typically be a variety of types including things like strings, numbers, booleans, arrays, or objects, and their structures typically align with objects developers are working with in code. Because of their variety of field value types and powerful query languages, document databases are great for a wide variety of use cases and can be used as a general-purpose database. They can horizontally scale-out to accommodate large data volumes. MongoDB is consistently ranked as the world’s most popular NoSQL database according to DB-engines and is an example of a document database.
- Key-value databases are a simpler type of database where each item contains keys and values. A value can typically only be retrieved by referencing its key, so learning how to query for a specific key-value pair is typically simple. Key-value databases are great for use cases where you need to store large amounts of data but you don’t need to perform complex queries to retrieve it. Common use cases include storing user preferences or caching. Redis and DynamoDB are popular key-value databases.
- Wide-column stores store data in tables, rows, and dynamic columns. Wide-column stores provide a lot of flexibility over relational databases because each row is not required to have the same columns. Many consider wide-column stores to be two-dimensional key-value databases. Wide-column stores are great for when you need to store large amounts of data and you can predict what your query patterns will be. Wide-column stores are commonly used for storing Internet of Things data and user profile data. Cassandra and HBase are two of the most popular wide-column stores.
- Graph databases store data in nodes and edges. Nodes typically store information about people, places, and things while edges store information about the relationships between the nodes. Graph databases excel in use cases where you need to traverse relationships to look for patterns such as social networks, fraud detection, and recommendation engines. Neo4j and JanusGraph are examples of graph databases.
BigData
Bigdata is a term used to describe a collection of data that is huge in size and yet growing exponentially with time. Big Data analytics examples includes stock exchanges, social media sites, jet engines, etc. It is natural to host a big data infrastructure in the cloud, because it provides unlimited data storage and easy options for highly parallelized big data processing and analysis.
GCP Platform provides multiple services that support big data storage and analysis. Possibly the most important is BigQuery, a high-performance SQL-compatible engine that can perform analysis on very large data volumes in seconds. GCP provides several other services, including Dataflow, Dataproc and Data Fusion, to help you create a complete cloud-based big data infrastructure.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!